Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome (EDS) is a complex genetic disorder. It affects connective tissues, leading to symptoms like hypermobility and fragile skin.
Scoliosis, a condition where the spine curves sideways, often accompanies EDS. This connection is due to the tissue abnormalities in EDS.
Understanding the link between EDS and scoliosis is crucial. It helps in managing symptoms and improving quality of life.
Individuals with EDS face unique challenges. These include chronic pain and mobility issues.
Diagnosis and treatment require a comprehensive approach. This involves healthcare professionals from various fields.
Early detection of scoliosis in EDS patients is vital. It can prevent severe complications and improve outcomes.
Management strategies include physical therapy and, in some cases, surgery. These aim to alleviate symptoms and enhance daily functioning.
Support and education are key. They empower patients and families to navigate the complexities of EDS and scoliosis.
Understanding Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome (EDS)
Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome (EDS) comprises a group of genetic disorders. These disorders primarily affect connective tissues, such as skin, joints, and blood vessel walls. EDS is classified into several types, each with varying symptoms and degrees of severity.
The most common features of EDS include:
- Hyperflexibility of joints
- Delicate, easily bruised skin
- Tissue fragility
People with EDS often experience chronic pain and joint instability. These symptoms can complicate daily life and affect physical activities. Managing these symptoms is essential for maintaining mobility and quality of life.
Understanding the specific type of EDS is crucial for treatment. Each type presents unique challenges and requires tailored management strategies. Genetic testing plays a significant role in diagnosing different types of EDS. This testing aids in developing appropriate care plans for patients.
Regular monitoring by healthcare professionals helps in managing EDS effectively. It ensures timely interventions and adjustments to treatment plans. Overall, education and awareness can empower individuals living with EDS, helping them lead fulfilling lives.
What Is Scoliosis?
Scoliosis is a condition characterized by an abnormal curvature of the spine. Instead of a straight line, the spine curves into an “S” or “C” shape. This curvature can occur at any part of the spine but most commonly affects the chest area.
Common signs of scoliosis include:
- Uneven shoulders or waist
- A protruding shoulder blade
- A visible spine curve
Scoliosis can develop during childhood or adolescence, often noticed during growth spurts. It can also arise from conditions affecting connective tissue, like EDS. Scoliosis varies in severity, from mild cases requiring monitoring to severe cases needing intervention. Understanding scoliosis involves recognizing its impact on posture and potential complications, such as respiratory issues or chronic pain. Early detection can lead to better management and improved outcomes.
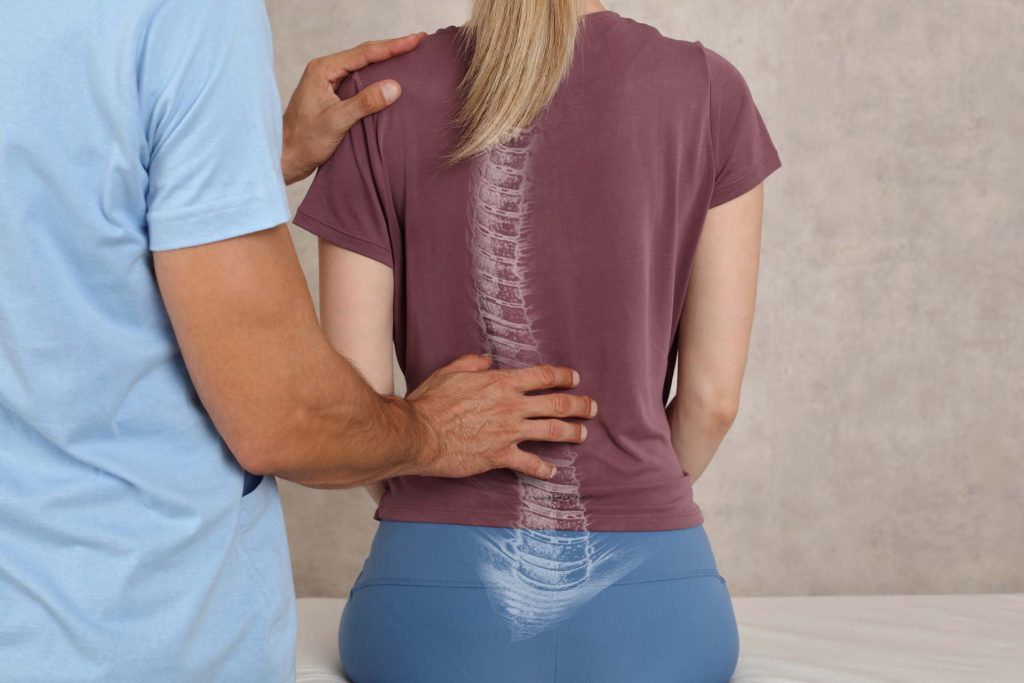
The Link Between EDS and Scoliosis
Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome (EDS) is closely associated with scoliosis due to its effects on connective tissue. The body’s connective tissues provide structural support, and EDS causes these tissues to weaken, increasing the risk of scoliosis. This relationship is crucial for understanding the physical manifestations and management of EDS.
The hypermobile type of EDS is most commonly linked with scoliosis. This type is characterized by joint hypermobility, skin elasticity, and tissue fragility. These symptoms can exacerbate spinal problems, leading to scoliosis. Hypermobile joints may lead to muscle imbalances, thus affecting the spine’s alignment.
Several factors contribute to scoliosis development in EDS patients, including:
- Soft tissue laxity
- Muscular imbalances
- Abnormal spinal growth patterns
The intertwining of EDS and scoliosis presents unique challenges. Patients may experience more rapid progression of spinal curves, especially during growth spurts. Understanding this connection helps in early detection and intervention, potentially mitigating severe effects. Tailored management plans can address these dual conditions, improving patient outcomes and quality of life.
Prevalence and Types of Scoliosis in EDS
Scoliosis is quite common among individuals with Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome. The prevalence varies significantly across different studies, but it’s a recognized complication. Some studies suggest that more than half of EDS patients may develop scoliosis at some point in their lives.
There are various types of scoliosis observed in EDS patients. These can range from mild to severe. The most common is structural scoliosis, where the spinal curve is rigid. This type often develops during growth spurts in children and adolescents.
Types of scoliosis seen in EDS include:
- Structural scoliosis
- Thoracolumbar scoliosis
- Cervical scoliosis
Each type requires specific attention due to the diverse presentation of symptoms and progression. Identifying the type early can guide the most effective treatment plan, preventing further complications and improving patient quality of life. Understanding these categories helps in tailoring patient care and optimizing outcomes.
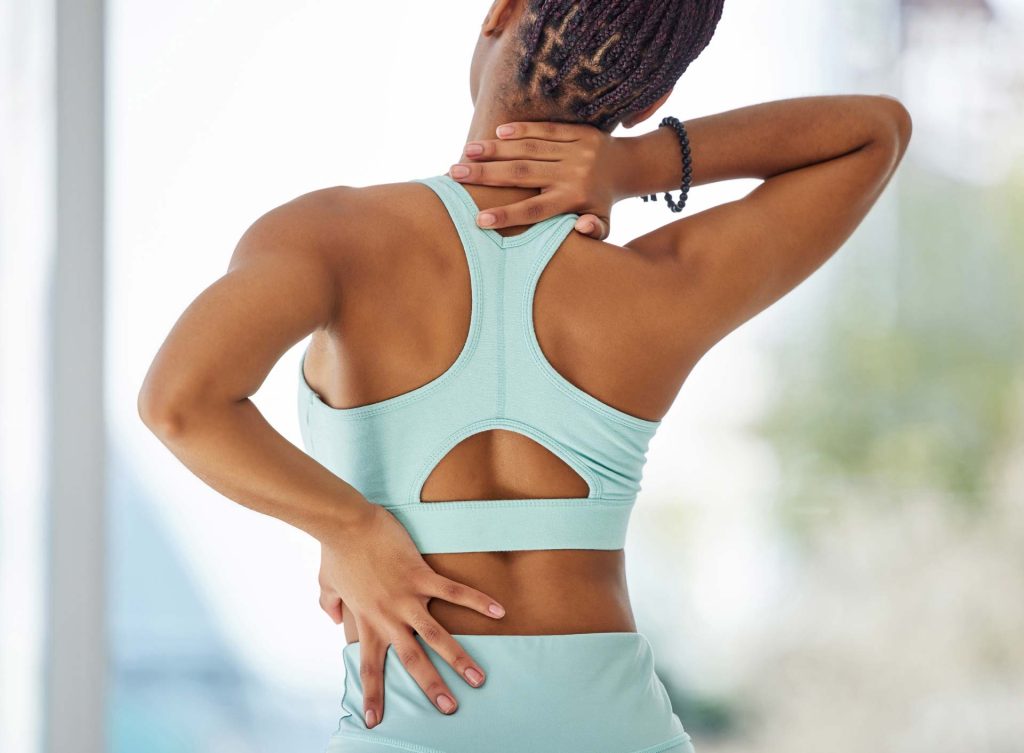
Symptoms of Scoliosis in Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome
Recognizing scoliosis symptoms in EDS patients is essential. These symptoms can manifest differently than in idiopathic cases, often linked to the underlying connective tissue disorder. The symptoms might not be immediately apparent but can evolve and become more noticeable over time.
Common symptoms in EDS-related scoliosis include:
- Back pain
- Uneven shoulders
- Visible spinal curve
EDS patients might also experience hypermobility and skin elasticity, complicating scoliosis symptoms further. Monitoring these symptoms is crucial, as early detection can lead to more effective management and intervention. Keeping a close eye on physical changes ensures timely adjustments to treatment plans and can help slow progression and reduce complications.

Diagnosing Scoliosis in EDS Patients
Diagnosing scoliosis in patients with Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome requires a detailed approach. It often begins with a comprehensive physical examination, where the physician looks for signs of scoliosis. These signs might include asymmetrical shoulders or a noticeable curvature in the spine.
A detailed medical history is crucial in the diagnostic process. This includes understanding family history, as genetics play a significant role in EDS. Physicians may inquire about past symptoms and any related health issues that could influence a scoliosis diagnosis.
Imaging tests, such as X-rays or MRIs, are vital for confirming scoliosis. These tests help quantify the degree of curvature and assess the severity of spinal misalignment. With accurate diagnosis, healthcare providers can craft personalized treatment plans tailored to each patient’s unique situation.
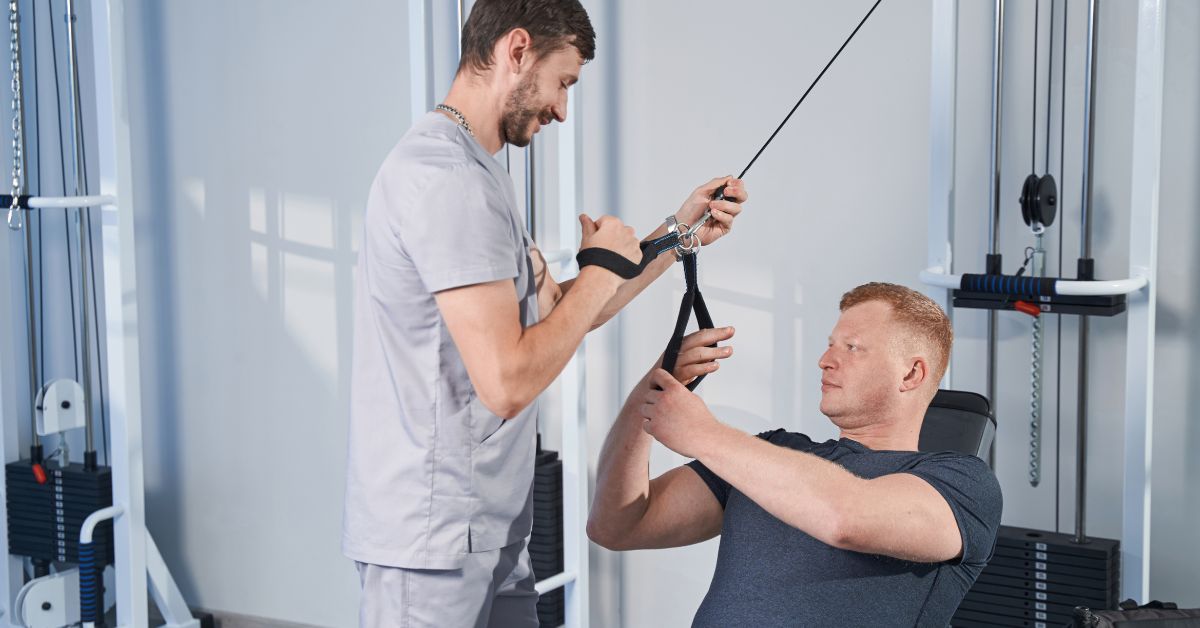
Treatment Options for Scoliosis in EDS
Managing scoliosis in Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome involves a range of treatment options. These approaches are tailored to the severity and individual needs of the patient. Non-surgical methods are usually the first line of defense.
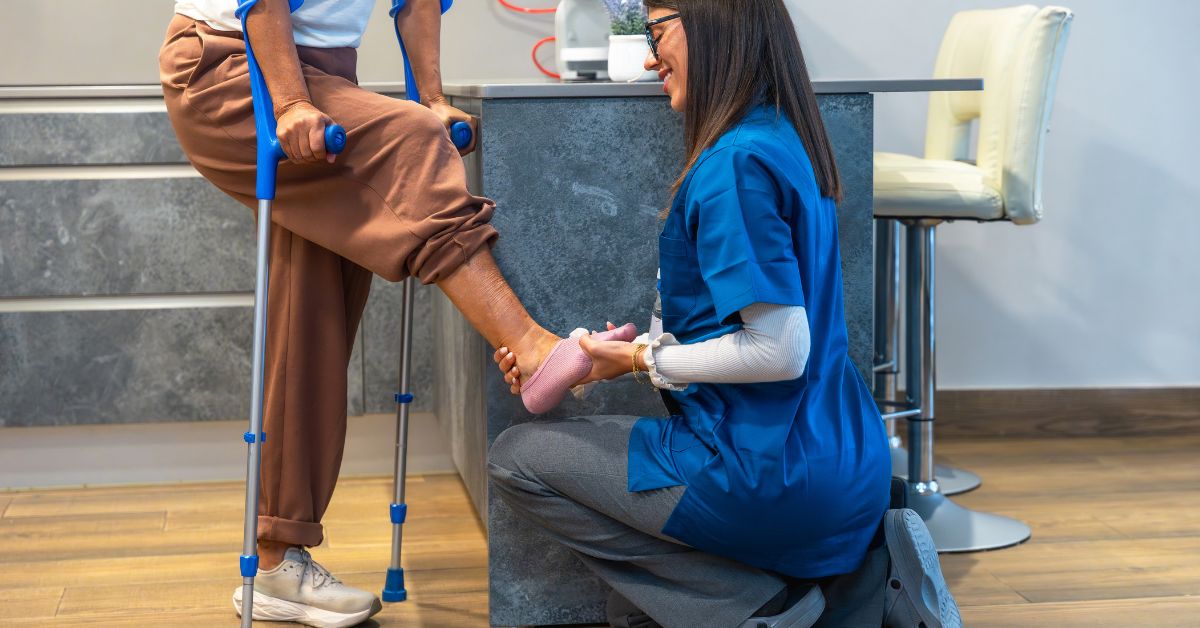
Physical therapy plays a vital role in managing scoliosis in EDS. It helps in strengthening muscles and improving flexibility, which can reduce discomfort. Therapists design specific exercises to stabilize the spine and alleviate strain.
Bracing is another common strategy, particularly for children experiencing growth spurts. Braces help prevent further curvature of the spine and aid in managing progression. This method is crucial during periods of rapid development.
In severe cases, surgical intervention becomes necessary. Surgery aims to correct the spinal curvature and prevent further health complications. Risks and benefits are carefully weighed before proceeding.
Key treatment strategies include:
- Physical Therapy: Exercises to strengthen and increase flexibility.
- Bracing: Used mainly in growing children.
- Surgery: Considered for severe scoliosis cases.
Physical Therapy and Rehabilitation
Physical therapy is essential in managing scoliosis for those with EDS. Regular sessions can lead to improved strength and posture. This therapy aims to reduce pain and enhance daily life.
Therapists create personalized exercise routines for patients. These routines often include flexibility exercises and strengthening activities. This helps patients maintain better spinal alignment.
Benefits of physical therapy include:
- Enhanced muscle strength
- Improved flexibility
- Reduction in pain
Bracing and Non-Surgical Management
Bracing offers a non-invasive method for managing scoliosis in EDS patients. It primarily helps during growth spurts in children. The brace prevents further curvature and supports spinal alignment.
Non-surgical management focuses on maintaining quality of life. Lifestyle adjustments, such as avoiding excessive strain and maintaining a healthy weight, are key. Regular monitoring by healthcare professionals is also critical.
Key aspects of non-surgical management include:
- Use of braces in children
- Lifestyle and activity modifications
- Regular medical follow-up
Surgical Considerations and Risks
Surgery for scoliosis in EDS patients is considered when other options fail. It involves correcting the curvature and stabilizing the spine. The decision to undergo surgery involves careful planning and discussion.
There are specific risks associated with scoliosis surgery in EDS patients. These may include delayed wound healing due to tissue fragility. Surgeons assess each case to minimize potential complications.
Before surgery, a multidisciplinary team evaluates the patient. The team includes geneticists, orthopedists, and physical therapists. This collaboration ensures comprehensive care and reduces surgical risks.
Surgical considerations involve:
- Correcting severe spinal curvature
- Assessing risks like delayed healing
- Multidisciplinary team approach
Pain Management and Quality of Life
Pain management is a vital aspect of living with scoliosis in EDS. Persistent discomfort can affect daily activities and overall well-being. Effective pain management strategies are essential for improving life quality.
A combination of approaches is often used to manage pain. Medications, such as pain relievers or anti-inflammatories, can provide relief. Additionally, lifestyle changes like regular exercise and stress reduction can help.
Quality of life can be enhanced through supportive practices:
- Medications: Pain relief and anti-inflammatory drugs
- Exercise: Regular physical activity to improve mobility
- Mindfulness: Stress-reduction techniques for emotional well-being
Psychological and Social Impact
Living with EDS and scoliosis can have significant psychological and social effects. The emotional burden of chronic conditions may lead to anxiety or depression. It’s crucial to address these mental health challenges promptly.
Social connections can also be affected. Individuals may feel isolated or misunderstood. Support from family, friends, and mental health professionals is beneficial.
Helpful strategies include:
- Therapy: Talking with a counselor or therapist
- Support groups: Connecting with others facing similar challenges
- Community involvement: Engaging in social activities to build support networks
Living with EDS and Scoliosis: Daily Management Tips
Managing EDS and scoliosis involves mindful daily practices. Prioritizing self-care can improve overall well-being. Consistent habits are crucial for managing symptoms effectively.
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle is vital. This includes regular physical activity tailored to your comfort level. Nutrition also plays a crucial role in maintaining energy and strength.
Here are some daily management tips:
- Exercise regularly: Engage in low-impact activities like swimming or yoga.
- Dietary choices: Maintain a balanced diet rich in nutrients.
- Postural care: Use ergonomic furniture to support posture.
- Listen to your body: Rest when necessary and avoid overexertion.
The Role of Genetics and Family History
Genetics play a pivotal role in Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome. EDS is primarily an inherited condition. Understanding your family history can provide valuable insights.
Recognizing genetic patterns helps in early diagnosis. It also aids in personalized management strategies. Being aware of familial tendencies is critical.
Here’s what to consider:
- Family history review: Note any relatives with similar symptoms.
- Genetic counseling: Seek professional guidance for risk assessment.
- Regular updates: Keep your healthcare provider informed of any changes in family medical history.
Multidisciplinary Care and Support Resources
Navigating Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome and scoliosis requires a team effort. A multidisciplinary approach ensures comprehensive care, addressing various needs.
The involvement of different specialists helps manage the complexities of EDS. Collaboration is key to effective treatment.
Consider the following for support:
- Geneticists: Offer insights into genetic influences.
- Orthopedists: Assess and manage scoliosis.
- Physical therapists: Design personalized exercise programs.
- Mental health professionals: Support psychological well-being.
- Patient support groups: Provide community and sharing of experiences.
Advances in Research and Future Directions
Research in Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome and scoliosis is ever-evolving. Scientists focus on understanding the genetic basis of these conditions.
Key research areas include:
- Genetic Testing: Advancements improve diagnosis and classification.
- Biomaterial Innovations: Enhance surgical outcomes.
- Targeted Therapies: Aim to address specific EDS complications.
- Gene Therapy: Holds promise for future treatments.
- Collaborative Research: Combines expertise for holistic solutions.
These efforts aim to provide better management strategies and improve quality of life for those with EDS and scoliosis. As we move forward, continued research will be crucial in devising innovative treatments.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome?
Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome (EDS) is a genetic disorder affecting connective tissues. It causes hypermobility and fragile skin.
How does scoliosis relate to EDS?
EDS affects connective tissues, increasing scoliosis risk. Spinal curvature is more common in EDS patients.
What are scoliosis symptoms in EDS?
Symptoms include back pain, uneven shoulders, and visible spine curvature. Severity varies by individual.
How is scoliosis diagnosed in EDS?
Diagnosis involves physical exams, medical history, and imaging tests like X-rays or MRIs.
Are there specific treatments for scoliosis in EDS?
Options include physical therapy, bracing, or surgery. Treatment depends on severity and patient needs.
Can scoliosis progress?
Yes, especially during growth spurts in children. Regular monitoring is vital for management.
Is genetic testing recommended?
Genetic testing helps in diagnosing EDS. It aids in understanding scoliosis risk and management.
How can I improve my quality of life with EDS and scoliosis?
Adopt lifestyle changes, pursue physical therapy, and seek psychological support. Pain management and community support are essential.
Conclusion
The relationship between Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome and scoliosis highlights the complexity of connective tissue disorders. Understanding this link is vital.
Early detection, personalized treatment, and ongoing management are crucial in addressing scoliosis in EDS. By integrating medical, physical, and psychological care, individuals with EDS and scoliosis can significantly improve their quality of life.




https://shorturl.fm/mbYs3
https://shorturl.fm/yJ1gB
https://shorturl.fm/e8nUu
https://shorturl.fm/4gnuG
https://shorturl.fm/e2lpD
https://shorturl.fm/eJR5c
https://shorturl.fm/rQEdv
https://shorturl.fm/9VaeT
https://shorturl.fm/8Mwyk
https://shorturl.fm/F5TLP
https://shorturl.fm/jQw5m
https://shorturl.fm/6W7I9
https://shorturl.fm/rCyrz
https://shorturl.fm/A3ovu
The comprehensive approach outlined here highlights the importance of multidisciplinary care in managing Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome
with scoliosis 🩺✨. I’d be interested to see more emphasis on the
role of personalized physical therapy programs that adapt over time as the condition progresses—especially how integrating
patient feedback can optimize outcomes. It’s
encouraging to see such a holistic framework in place!
https://shorturl.fm/oGMWI
https://shorturl.fm/sO0KA
https://shorturl.fm/eqNlO
https://shorturl.fm/kvMep
https://shorturl.fm/mIe7U
https://shorturl.fm/agdaT
https://shorturl.fm/yS27B
https://shorturl.fm/FC6Ji
https://shorturl.fm/l0B3J
https://shorturl.fm/zwR9C
https://shorturl.fm/uiqSC
https://shorturl.fm/khDkz
https://shorturl.fm/2JhuY
https://shorturl.fm/0Irh1
https://shorturl.fm/eLFnG
Yo, anyone tried pakwingame? I’m looking for a new game to get addicted to. I’ll check it out pakwingame.
Alright crew, who’s feeling lucky? Check out luckypkr, might be your lucky day. Get lucky at luckypkr.
Yo, awin68 is legit! Good selection of games and the site layout is clean. I’d recommend it if you’re looking for a reliable spot to wager. Hit up awin68