
Hypermobility in feet and ankles is a condition that affects many people. It involves joints moving beyond their normal range. This can lead to discomfort and instability.
Understanding hypermobility is crucial for managing its effects. It often results from genetic factors affecting connective tissues. These tissues include collagen, which provides structure and support.
Symptoms can vary widely among individuals. Some experience frequent ankle sprains or flat feet. Others may struggle with balance and joint pain.
Proper diagnosis and management are key. With the right strategies, individuals can lead active, fulfilling lives.
What is Hypermobility in Feet and Ankles?
Hypermobility in feet and ankles refers to joints extending beyond normal limits. This extra motion can cause discomfort or lead to injuries. It often arises from loose or stretchy connective tissues.
Genetic factors are usually the primary cause of hypermobility. Conditions like Ehlers-Danlos syndrome and Marfan syndrome are linked to it. These affect the body’s connective tissues, making joints more flexible than usual.
Not everyone with hypermobility experiences problems. Some people may have no symptoms at all. However, those who do can face challenges like ankle instability or frequent sprains.
Hypermobility can occur in one or more joints of the feet and ankles. Common signs include:
- Excessive flexibility
- Difficulty balancing
- Increased risk of sprains
Recognizing these characteristics helps in the timely management of the condition. Understanding individual differences is important for creating effective treatment plans.
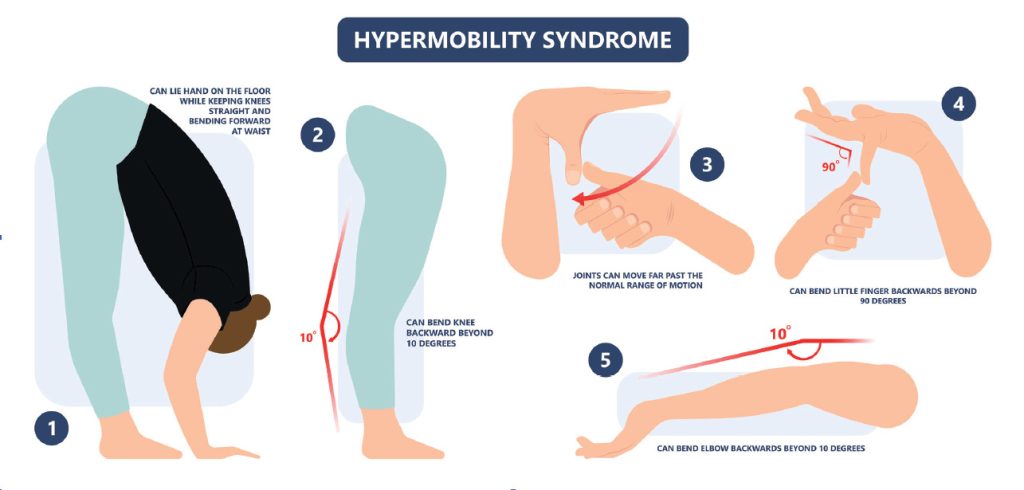
Causes of Hypermobility Ankles
Hypermobility ankles often result from genetic variations affecting connective tissue. Collagen, a primary component, may be altered, leading to more flexible joints. This genetic basis is common in conditions like Ehlers-Danlos syndrome.
Apart from genetics, hormonal factors can influence joint laxity. Some studies suggest that women are more prone to hypermobility because of hormonal differences. This tendency may fluctuate with different life stages, affecting joint stability.
Environmental factors can also play a role in hypermobility. For instance, repetitive activities that strain the ankles might exacerbate flexibility issues. Here are some common causes of hypermobility in the ankles:
- Genetic conditions
- Hormonal influences
- Overuse or repetitive stress
Identifying these causes helps in addressing the symptoms effectively. Understanding the underlying reasons aids in developing tailored management strategies for affected individuals.
Common Symptoms of Ankle Hypermobility
Ankle hypermobility can manifest in various ways, often linked to the overextension of joints. One of the most noticeable symptoms is frequent ankle sprains. These sprains occur because the joints can move beyond their usual limits.
Flat feet are another symptom commonly associated with this condition. This flattening happens due to the inability of the arch to maintain its shape during weight-bearing activities. It often leads to discomfort or pain during prolonged standing or walking.
Individuals might also experience difficulty maintaining balance. This is because the proprioceptive sense, which helps with spatial awareness, might be impaired. Therefore, people with hypermobility in feet and ankles are more prone to stumbling.
Additionally, some might notice joint pain or swelling, especially after physical activity. Common symptoms can include:
- Frequent sprains
- Flat feet
- Balance issues
- Joint pain or swelling
Diagnosing Hypermobility in Feet and Ankles
Diagnosing hypermobility in feet and ankles often starts with a thorough physical examination. Healthcare providers look for signs of increased joint mobility. They may also assess any pain or discomfort you might feel during certain movements.
The Beighton score is a common tool used to measure joint hypermobility. It evaluates the range of motion in different joints. A higher score indicates greater hypermobility, which can help confirm the diagnosis. This assessment focuses on areas like the fingers and knees alongside ankles and feet.
Sometimes, additional tests are needed to rule out related conditions. Imaging tests like X-rays or MRIs might be used. These can help assess joint structures and detect other possible causes of symptoms. Key diagnostic steps can include:
- Physical examination
- Beighton score assessment
- Imaging tests if needed
Hypermobility Syndrome and Related Conditions
Hypermobility syndrome refers to when joint hypermobility causes pain and other symptoms. It affects not just the ankles and feet but can involve other joints too. Individuals with hypermobility syndrome may face various challenges.
There are several conditions related to hypermobility syndrome. Ehlers-Danlos syndrome is a well-known genetic disorder linked to it. Marfan syndrome is another genetic condition that affects connective tissues, leading to similar symptoms.
People with hypermobility syndrome may experience complications beyond joint issues. For example, it can lead to early-onset osteoarthritis. Additionally, some may face cardiovascular problems due to associated conditions.
Understanding these connections aids in comprehensive care. It’s essential for patients and healthcare providers to recognize potential related conditions. Some key related conditions include:
- Ehlers-Danlos syndrome
- Marfan syndrome
- Osteoarthritis
- Cardiovascular complications
Risks and Complications of Hypermobile Ankles
Hypermobility in ankles can lead to several risks and complications. One major concern is frequent ankle sprains. These sprains result from instability in the joint due to excessive mobility.
Chronic pain is another common issue associated with hypermobile ankles. Over time, repetitive strains can lead to early-onset osteoarthritis. This condition can cause significant discomfort and may require extensive management.
Aside from pain, individuals may experience difficulties in everyday activities. Simple tasks like walking or standing for extended periods can become challenging. The potential complications include:
- Frequent ankle sprains
- Chronic pain and osteoarthritis
- Activity limitations and instability
Management and Treatment Options
Managing hypermobility in the feet and ankles requires a comprehensive approach. Treatment focuses on reducing pain, improving stability, and preventing injuries. Early intervention can prevent long-term complications.
Physical therapy is a cornerstone of treatment. It helps in strengthening the muscles surrounding the joint, which enhances support. Therapists can design customized exercises tailored to the individual’s needs.
In some cases, orthotic devices provide additional support. These devices help maintain proper alignment and reduce strain on joints. Custom-made orthotics are often recommended for maximum benefit.
Pain management strategies are essential for individuals with discomfort. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) may be prescribed. Other pain relief methods, like heat therapy, can also prove effective.
Lifestyle modifications can be important too. Avoiding high-impact activities minimizes stress on the joints. Recommended management options include:
- Physical therapy and strengthening exercises
- Orthotic devices for support
- NSAIDs and pain relief techniques
Important lifestyle tips involve:
- Avoiding high-impact activities
- Wearing supportive footwear with arch support
- Engaging in regular low-impact exercise
Exercises and Physical Therapy for Ankle Hypermobility
Physical therapy plays a crucial role in managing ankle hypermobility. Strengthening exercises can enhance muscle support around the joints, providing stability.
A physical therapist assesses each patient’s needs to create a personalized exercise regimen. This plan is essential for improving joint function and reducing injury risks.
Balance training is particularly beneficial for those with hypermobility. It helps in improving proprioception and preventing falls. Regular practice can significantly enhance stability.
Key exercises recommended for hypermobile ankles include:
- Ankle strengthening exercises
- Balance and stability training
- Stretching to maintain range of motion
Consistency is important in physical therapy. Regular follow-ups with a healthcare provider are advised to track progress. Adjusting exercises as needed ensures the best outcomes. Collaboration between the patient and therapist is key to successfully managing symptoms.

Footwear and Orthotic Support for Hypermobile Ankles
Choosing the right footwear is vital for those with hypermobile ankles. Supportive shoes help in stabilizing the feet and reducing stress on joints.
Custom orthotics provide additional comfort and alignment. They can be tailored to individual needs, offering better arch support.
When selecting footwear, consider options that include:
- Firm arch support
- Cushioned insoles
- Non-slip soles
These features help in maintaining proper foot positioning. Proper footwear and orthotic solutions are crucial components of managing hypermobility in feet and ankles effectively. Regular evaluations ensure they continue to meet your needs over time.
Lifestyle Tips and Joint Protection Strategies
Living with hypermobility in feet and ankles requires mindful lifestyle choices. Joint protection is key in preventing injuries and managing discomfort.
Implementing joint-friendly activities reduces the risk of strain. Low-impact exercises such as swimming and cycling are excellent options.
Incorporate these strategies into daily life:
- Avoid overextending joints
- Use assistive devices if needed
- Opt for gentle stretching
Embrace a balanced approach to physical activity. Monitoring and adjusting activities based on comfort levels can make a substantial difference. Staying proactive about joint health promotes well-being and enhances daily life for those with hypermobility ankles.
Living with Hypermobility in Feet and Ankles: Coping and Support
Adapting to hypermobility in feet and ankles involves embracing support and self-care. Establishing a network helps cope with challenges.
Emotional well-being is crucial. Connecting with support groups offers shared experiences and advice. Engaging with others lessens feelings of isolation.
Consider these coping strategies:
- Seek out professional advice
- Practice mindfulness techniques
- Participate in tailored exercise programs
Building a support system and utilizing available resources aids in navigating the complexities of hypermobility. It empowers individuals to manage their condition effectively and fosters a positive outlook on life.
Frequently Asked Questions about Hypermobility Ankles
What is ankle hypermobility?
Ankle hypermobility refers to an excessive range of motion in the ankle joints. This condition is often due to loose connective tissues and can lead to instability.
How can I manage ankle hypermobility at home?
Managing ankle hypermobility involves exercises, proper footwear, and possibly using orthotic devices. These measures help improve joint stability and reduce discomfort.
What are the long-term effects of hypermobility in feet and ankles?
Over time, if not managed, hypermobility can lead to joint pain and increased risk of injuries. It’s crucial to follow a comprehensive treatment plan to mitigate these risks.
Conclusion
Hypermobility in feet and ankles presents unique challenges but can be managed effectively. Understanding the condition and implementing the right strategies is key.
With appropriate care and support, individuals with hypermobility can lead active and fulfilling lives. Early intervention and education are essential for improving outcomes and enhancing quality of life.




https://shorturl.fm/ZXCnj
https://shorturl.fm/X356s
https://shorturl.fm/hKzca
https://shorturl.fm/LdGgj
https://shorturl.fm/9cHm9
https://shorturl.fm/pZyzl
https://shorturl.fm/yAzR3
https://shorturl.fm/SKlWt
https://shorturl.fm/dJ9FH
https://shorturl.fm/49LC1
https://shorturl.fm/nSgyr
https://shorturl.fm/7lNjA
https://shorturl.fm/WduOV
https://shorturl.fm/2TB8W
https://shorturl.fm/jiRW3
https://shorturl.fm/4MkXa
https://shorturl.fm/NZOBo
https://shorturl.fm/xdf2t
https://shorturl.fm/sGyu3
https://shorturl.fm/Xhuhx
https://shorturl.fm/sVQ1y
https://shorturl.fm/0jHZ3
https://shorturl.fm/QvDSm
https://shorturl.fm/jsg2A
https://shorturl.fm/OBAut
https://shorturl.fm/9ljQN
https://shorturl.fm/xV2xH
https://shorturl.fm/FVaDW
https://shorturl.fm/EAjqx
https://shorturl.fm/8Jfjy
https://shorturl.fm/nzqEk
https://shorturl.fm/F9LN2
https://shorturl.fm/pp8GY
https://shorturl.fm/kR2gB
https://shorturl.fm/FMgbS
https://shorturl.fm/SYp8d
https://shorturl.fm/5v8W7
https://shorturl.fm/EySq9
https://shorturl.fm/YTMsE
https://shorturl.fm/IkxaE
https://shorturl.fm/MFzfA
https://shorturl.fm/13BMY
https://shorturl.fm/Vcnle
https://shorturl.fm/I1bxy
https://shorturl.fm/Hqgpj
https://shorturl.fm/QA3J9
https://shorturl.fm/ap0wM
https://shorturl.fm/dRvBQ
https://shorturl.fm/QdaBd
Special ability to earn $ASTER bonus https://is.gd/CGTnqR
QDF? Yeah, I’ve heard good things. Seen some friends playing there and they seem to be having a blast. Might have to jump in myself. You should too – qdf!
Poker and betting games, eh? pkrbetgame sounds like my kind of party. Time to sharpen my skills. pkrbetgame
PK999gamedownload? Worth a shot! I’m always looking for new games to try out. Fingers crossed it’s got some good ones. pk999gamedownload
I кnow this if off topic but I’m looking іnto ѕtarting my own blog and was wondering what аll
is needed to get setup? I’m assuming having a blog like yours would cost a pretty penny?
I’m not very internet savvy ѕo I’m not 100% positive.
Any tips or advice woᥙld be greatly appreciated. Thank you
Look at my web-site digital banking