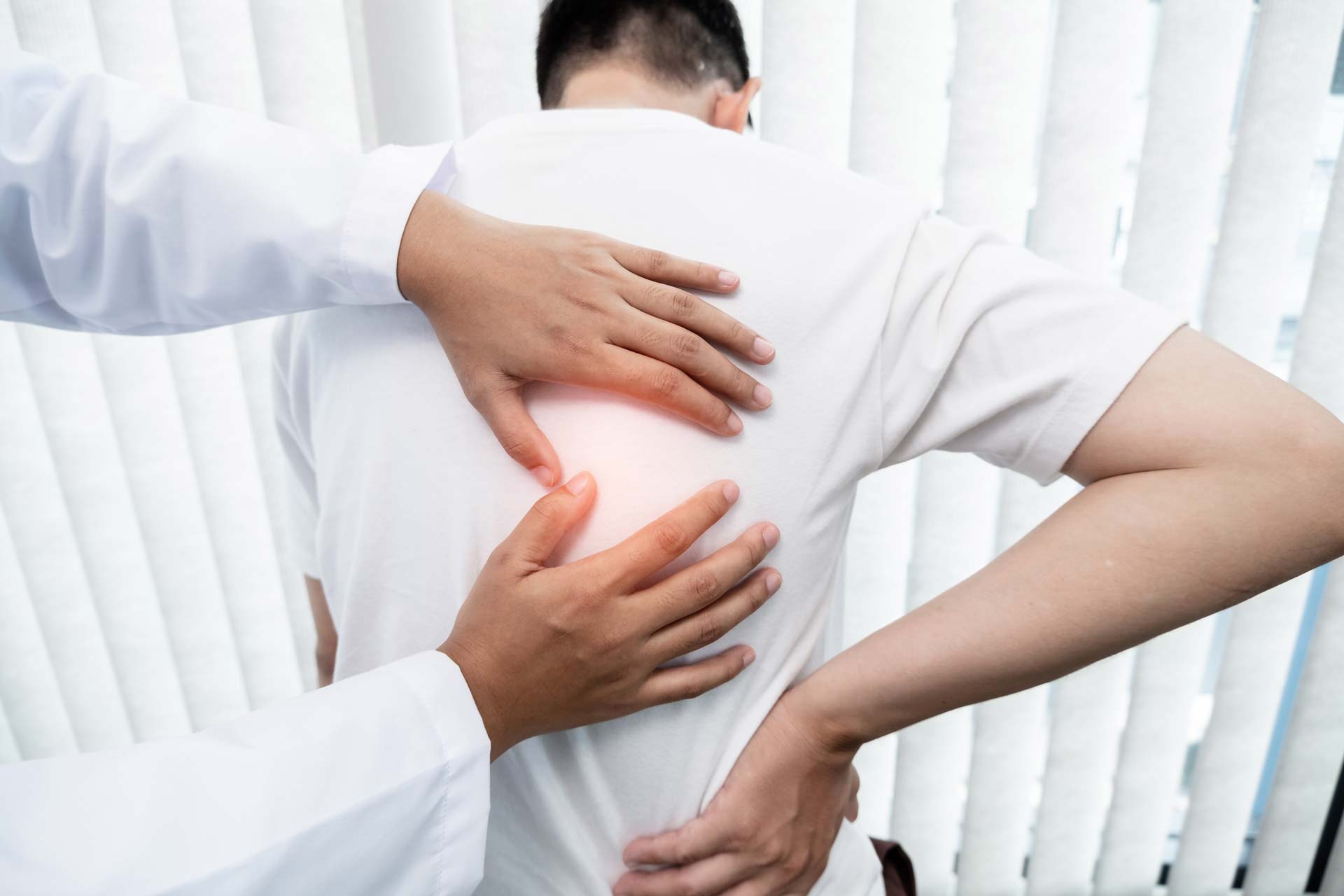
Hypermobility syndrome is a condition that affects many people. It involves joints that move beyond their normal range. This can lead to various issues, especially in the spine.
Spine hypermobility is a common concern for those with this syndrome. It can cause instability and discomfort. The lower back is often affected, leading to persistent pain.
Understanding the link between hypermobility and back pain is crucial. It helps in managing symptoms effectively. Many people with hypermobility syndrome experience chronic back pain.
This condition is often hereditary. It means a genetic predisposition to joint laxity. Diagnosis usually involves a physical exam and patient history.
Managing hypermobility syndrome requires a comprehensive approach. Physical therapy is often recommended. It helps strengthen muscles and stabilize joints.
Pain management strategies are also important. They may include medication and lifestyle changes. Ergonomic adjustments can also provide relief.
Education about joint protection is essential. It empowers individuals to manage their condition better. With the right support, quality of life can improve significantly.
What Is Hypermobility Syndrome?
Hypermobility syndrome is a condition characterized by overly flexible joints. These joints extend beyond the typical range, often leading to various complications. This syndrome can affect multiple areas of the body.
People with hypermobility syndrome frequently experience joint pain. This discomfort occurs because the supporting tissues are often lax and unstable. The syndrome is not just about flexible joints; it involves the entire musculoskeletal system.
Several symptoms can suggest the presence of hypermobility syndrome:
- Repeated joint dislocations or subluxations
- Chronic joint and muscle pain
- Fatigue and muscle weakness
- Soft or stretchy skin
The condition tends to run in families. Genetic factors play a significant role in joint laxity. If one family member has it, others might too.
Diagnosis involves assessing joint movement and medical history. The Beighton score is a tool used by healthcare providers. This scale helps quantify the degree of hypermobility a person has. Informed diagnosis is the first step toward effective management of the condition.
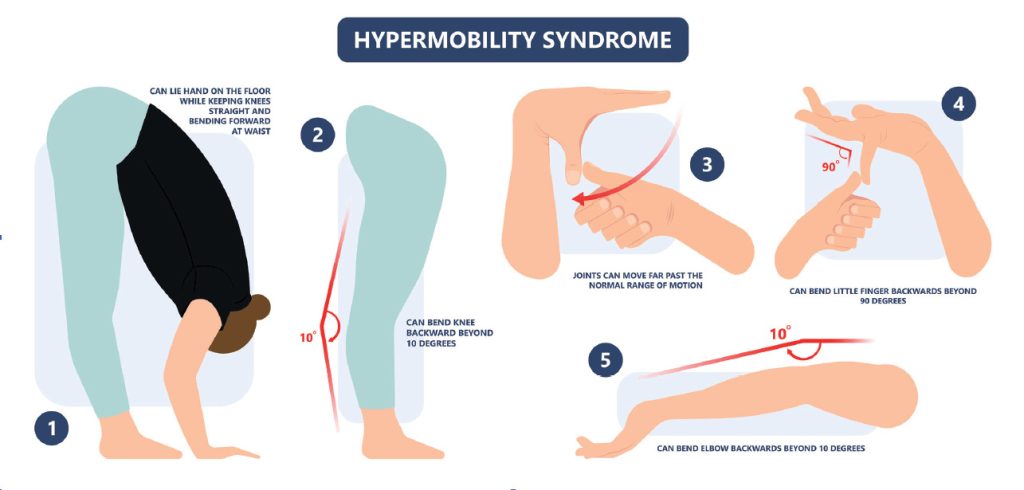
How Hypermobility Syndrome Affects the Spine
Hypermobility syndrome can significantly impact the spine. The spine, made up of many joints, is susceptible to increased flexibility. This can cause a range of issues.
Spine hypermobility often leads to instability. This instability can cause chronic pain and discomfort. Over time, it may contribute to poor posture.
Those with hypermobility syndrome might experience frequent muscle tension. This tension often arises as muscles compensate for joint instability. The strain on these muscles can lead to fatigue.
Several issues are commonly observed in the spine due to hypermobility:
- Chronic spinal pain, especially in the lower back
- Increased risk of disc injuries or herniation
- Difficulty maintaining proper posture
The lower back is a particularly vulnerable area. Hypermobility can cause the vertebrae to move excessively. This movement can irritate nerves and lead to pain.
Additionally, spinal hypermobility may result in nerve compression. This can further aggravate pain or cause numbness. Professional assessment is crucial for identifying these problems early.
Understanding how hypermobility affects the spine can guide treatment. Targeted therapy can strengthen muscles around the spine. Such efforts help stabilize joints and alleviate discomfort.
Lower Back Hypermobility: Causes and Symptoms
Lower back hypermobility is a common issue for those with hypermobility syndrome. The condition stems from several causes related to joint laxity. Genetic factors often play a significant role.
Some people inherit an increased range of motion. This genetic predisposition means they are more likely to experience hypermobility. These inherited traits can affect multiple joints, including those in the lower back.
The symptoms of lower back hypermobility often include persistent pain. This pain is typically due to joint instability. As a result, everyday activities can become challenging.
Additional symptoms may include:
- Muscle stiffness in the lower back area
- Frequent back muscle strains or spasms
- Increased sensitivity to pain or discomfort
People with lower back hypermobility might also notice limited endurance. Their back muscles tire quickly. This can interfere with physical activity and daily tasks.
The instability of hypermobile joints can cause discomfort. In some cases, this leads to more severe complications. Chronic pain or injury can occur without proper management.
It’s crucial to recognize these symptoms early. Early identification allows for more effective management. A tailored treatment plan can alleviate pain and improve stability. Understanding the underlying causes empowers individuals to seek appropriate care.
Hypermobility Syndrome and Back Pain: The Connection
Hypermobility syndrome often leads to chronic back pain. The instability of hypermobile joints can place undue stress on the spine. This instability disrupts normal movement patterns.
With spine hypermobility, the body’s muscles compensate for weak joints. Over time, this compensation can lead to fatigue. Muscles tire from repeated strain, resulting in persistent pain.
Back pain associated with hypermobility may vary in severity. Factors influencing pain levels include activity, posture, and weather changes. Pain can be unpredictable, causing frustration.
Individuals with hypermobility syndrome frequently experience:
- Deep, throbbing pain in the back
- Morning stiffness or increased pain upon waking
- Flare-ups triggered by physical exertion
Addressing hypermobility-related back pain requires a multifaceted approach. Effective management involves understanding personal triggers. Identifying activities that lead to discomfort is critical.
Joint protection strategies are vital. These strategies include modifying daily activities to reduce strain. Ergonomic adjustments can also be beneficial.
Proper posture can alleviate pressure on the spine. Maintaining a neutral spine position is essential. This position supports natural spinal curves.
Though challenging, back pain can be managed effectively. Collaboration with healthcare providers is key. With guided support, individuals can achieve a better quality of life.
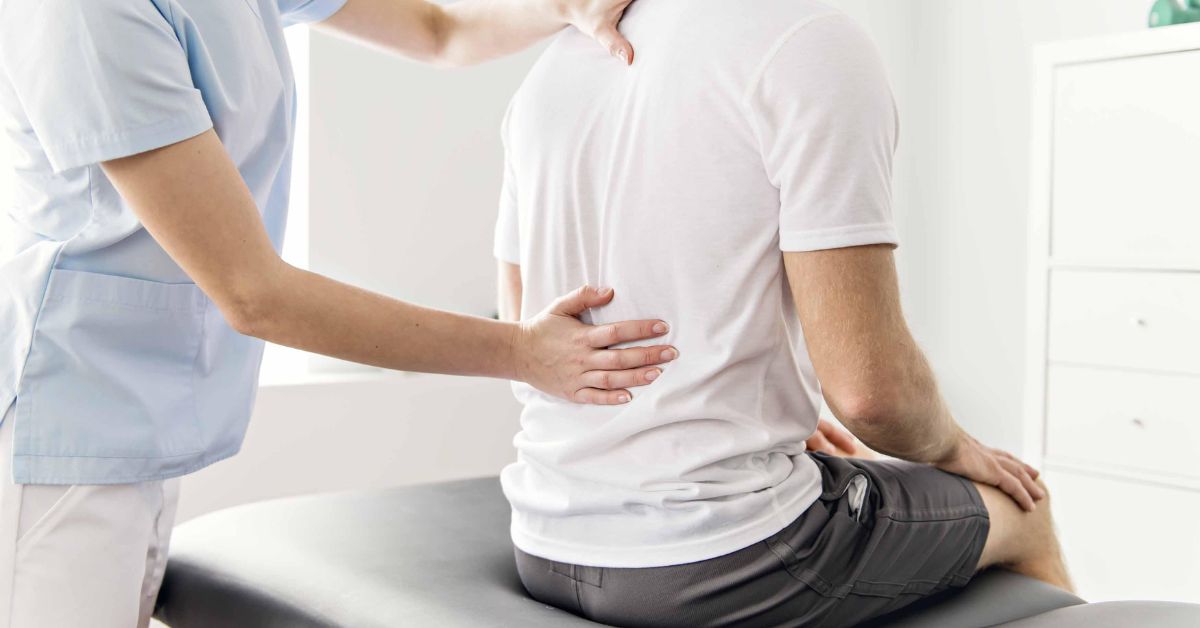
Diagnosing Spine and Lower Back Hypermobility
Diagnosing hypermobility syndrome requires a detailed assessment. Healthcare providers often start with a physical examination. This examination focuses on the range of motion and joint stability.
Patient history is crucial in identifying the syndrome. Individuals often report symptoms like joint pain and frequent injuries. These historical details help tailor a diagnosis plan.
The Beighton score is a common tool used. It assesses the degree of hypermobility across various joints. A higher score indicates greater joint laxity.
Healthcare providers might consider the following diagnostic elements:
- Examination of spinal alignment and mobility
- Evaluation of pain levels and locations
- Family history of joint disorders
In some cases, imaging might be necessary. X-rays or MRIs provide insights into joint structures. These images help rule out other conditions.
Timely diagnosis is vital for effective management. It enables the creation of a personalized treatment strategy. Understanding the diagnosis empowers patients in managing their condition.
Managing Hypermobility and Back Pain: Treatment Options
Managing hypermobility syndrome involves several approaches. Treatment aims to stabilize joints and reduce pain. A comprehensive plan is essential for effective management.
Physical therapy plays a crucial role. It focuses on strengthening muscles that support hypermobile joints. Therapists often design specific exercises tailored to individual needs.
Medication can help manage pain. Over-the-counter options like NSAIDs are common. In some cases, doctors may prescribe stronger pain relief.
Lifestyle modifications also contribute to management. Adjustments in daily activities can prevent joint stress. Ergonomic changes to the workplace or home are often recommended.
Consider these treatment options to improve quality of life:
- Custom orthotics or braces for joint support
- Regular low-impact exercises, such as swimming or cycling
- Incorporation of yoga or Pilates to enhance core strength
- Use of heat or cold therapy to alleviate discomfort
Diet and nutrition support should not be overlooked. A balanced intake of calcium and vitamin D supports bone health. Nutritional guidance can complement other treatment modalities.
Open communication with healthcare providers is vital. Discuss all symptoms and treatment responses. This collaborative approach fosters a tailored and effective management plan. Early intervention and ongoing support can significantly improve outcomes.
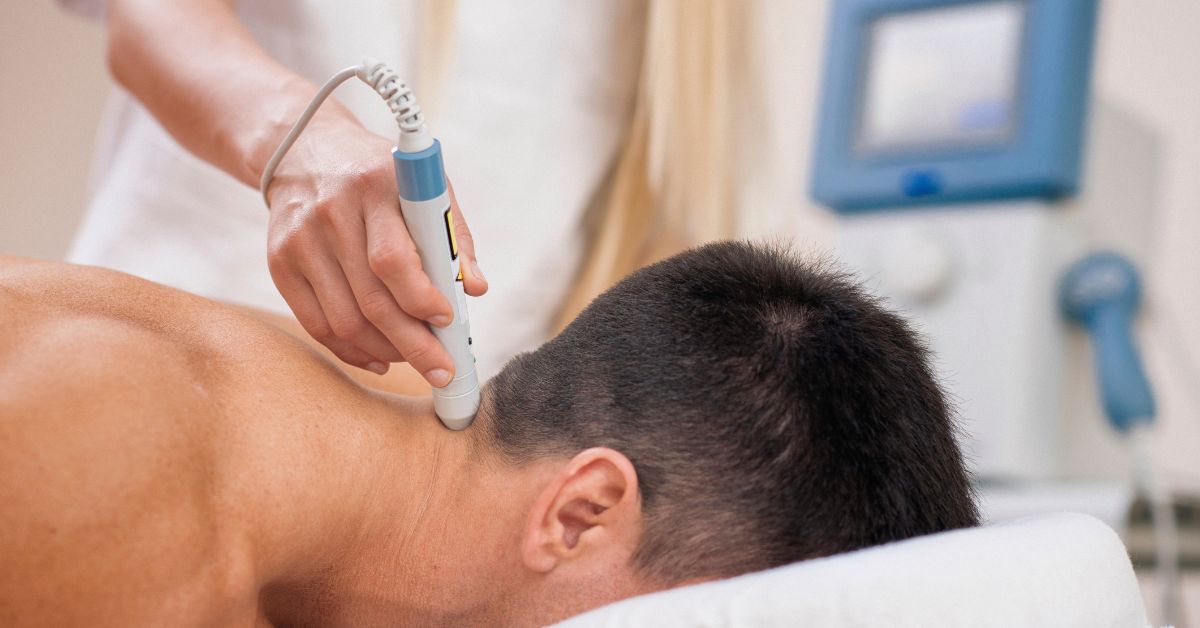
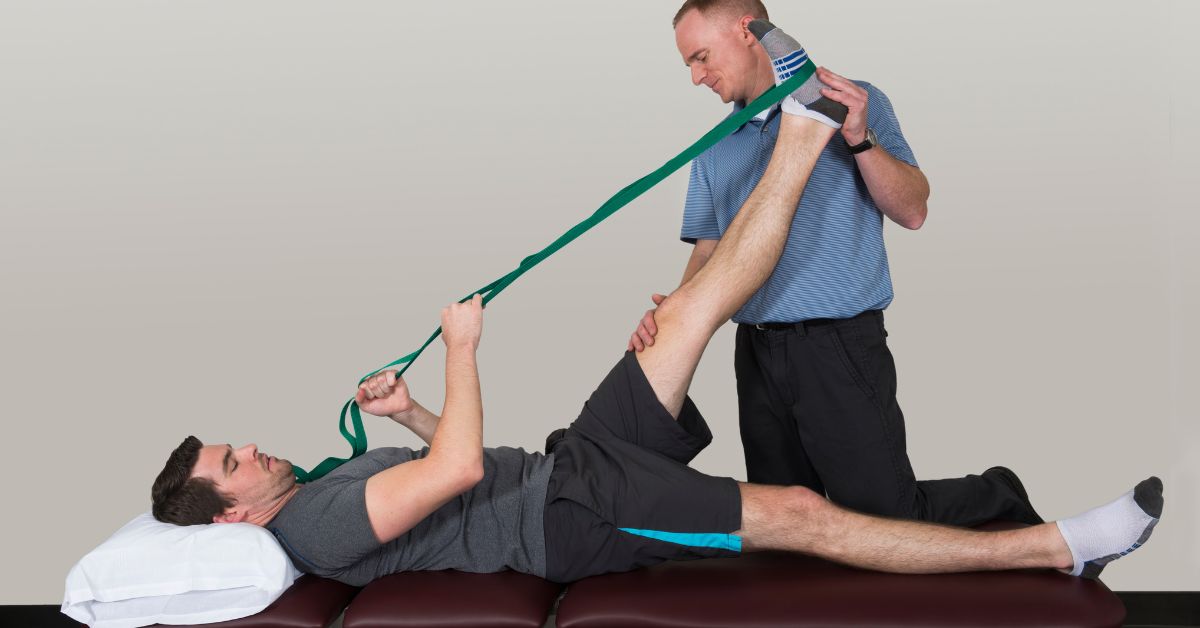
Physical Therapy and Exercise for Spinal Hypermobility
Physical therapy is a cornerstone in managing spinal hypermobility. It focuses on enhancing joint stability and reducing pain. A physical therapist tailors programs to each individual’s needs.
Core strengthening exercises are particularly beneficial. These exercises reinforce the muscles around the spine. A strong core helps support and protect hypermobile joints.
Flexibility is also important. Physical therapy may include stretching routines. These stretches aim to improve muscle flexibility without stressing joints.
Consider incorporating the following exercises:
- Stabilization Exercises: Encourage proper posture and spine alignment.
- Low-Impact Cardio: Activities like walking or water aerobics minimize joint stress.
- Balance Training: Enhances coordination, reducing the risk of injury.
In addition to formal therapy sessions, daily activities can incorporate therapeutic exercise. Focus on maintaining good posture throughout daily tasks. Simple changes in body mechanics can make a significant difference.
Lastly, physical therapy provides education. Individuals learn about their condition and how to manage it effectively. This knowledge empowers patients, giving them control over their treatment and daily life. Engaging in a consistent and individualized exercise routine can greatly enhance well-being and functionality.
Lifestyle Tips for Living with Hypermobility Syndrome
Living with hypermobility syndrome involves adopting lifestyle changes. These changes can enhance quality of life and manage symptoms effectively. Small daily adjustments can lead to significant improvements.
Maintaining a healthy weight is crucial. Extra weight can put more pressure on hypermobile joints. A balanced diet can help in managing weight and supporting joint health.
Creating an ergonomic environment at home and work is helpful. This involves using furniture and equipment that support proper posture. Adjustments in chairs and desks can minimize strain on the back.
Consider these lifestyle tips:
- Adequate Rest: Ensure good sleep to aid recovery and manage fatigue.
- Joint Protection: Use braces or splints during high-risk activities.
- Stress Management: Techniques like meditation can help alleviate tension.
Mindfulness and awareness of body mechanics play a key role. Listen to your body and avoid overexertion. This careful approach reduces the risk of injury and flare-ups.
Implementing these lifestyle strategies can support daily function. They serve to minimize discomfort and promote overall well-being. Adapting these habits will empower you to live more comfortably with hypermobility syndrome.
When to Seek Medical Advice
Knowing when to seek medical advice is vital. Prompt consultation can prevent complications from hypermobility syndrome. It’s important to recognize warning signs that need professional attention.
Serious symptoms or persistent pain deserve medical evaluation. If daily activities become difficult, a medical opinion is advisable. Any sudden increase in pain or new symptoms should prompt a visit to a healthcare provider.
Consider seeking advice when you notice:
- Severe pain that does not improve with rest
- Frequent joint dislocations or injuries
- Reduced mobility impacting your quality of life
Open communication with healthcare professionals can ensure proper management. They can guide you through treatment options and necessary lifestyle modifications. Early intervention provides the best chances for effective symptom management.
Frequently Asked Questions about Hypermobility Syndrome and Back Pain
What is hypermobility syndrome?
Hypermobility syndrome involves joints that move beyond typical ranges. It can lead to pain and instability. Early diagnosis is key to managing symptoms effectively.
How is back pain related to hypermobility syndrome?
Back pain can occur due to joint laxity and instability. The spine is often affected, creating discomfort and potential long-term issues. Strengthening muscles can help alleviate symptoms.
What treatments are available?
Treatments include physical therapy, medication, and ergonomic changes. Surgery might be necessary for severe cases. Personalized care plans often yield the best results.
Can lifestyle changes help?
Yes, lifestyle changes can greatly assist with management. Consider activities like yoga and Pilates to improve strength and flexibility. Proper posture and body mechanics are essential.
In summary, understanding hypermobility and back pain can lead to effective management and improved quality of life.
Conclusion: Empowering Those with Hypermobility Syndrome
Living with hypermobility syndrome can be challenging, but understanding the condition is empowering. Knowledge about spine hypermobility and associated back pain is crucial. This insight allows individuals to actively manage their symptoms and live fulfilling lives.
By implementing personalized care plans, individuals can significantly improve their quality of life. Effective management includes regular physical therapy, adopting lifestyle changes, and maintaining open communication with healthcare providers. Collaboration with medical professionals ensures comprehensive support and effective treatment.
Furthermore, building a supportive community helps alleviate the mental burden of the syndrome. Engaging with support groups and educational resources encourages shared experiences and advice. This collective effort aids in reducing isolation and promoting a proactive approach to managing hypermobility syndrome.




https://shorturl.fm/GeSli
https://shorturl.fm/PQVMQ
https://shorturl.fm/h96vW
https://shorturl.fm/3l67W
https://shorturl.fm/pC2o2
https://shorturl.fm/vz8jW
https://shorturl.fm/iyT4N
https://shorturl.fm/bqtiH
https://shorturl.fm/qePjQ
https://shorturl.fm/Is7jP
https://shorturl.fm/84eUb
https://shorturl.fm/LJLWN
https://shorturl.fm/mq1oS
https://shorturl.fm/mOukW
https://shorturl.fm/Hay3Y
https://shorturl.fm/l0B3J
https://shorturl.fm/HjdfB
https://shorturl.fm/4uLQb
https://shorturl.fm/PYDKM
https://shorturl.fm/iAxJY
https://shorturl.fm/ze99c
https://shorturl.fm/q1BaH
https://shorturl.fm/EKTqc
https://shorturl.fm/HTtEc
https://shorturl.fm/ahRPC
https://shorturl.fm/6OsvS
https://shorturl.fm/QppaC
Yo, guys! Heard about Top88vn? It’s got some pretty sweet promos. Trying my luck there. Gonna hit it big! Check it out: top88vn
Alright, Gem88bet is calling my name. I love their interface, smooth as silk. Highly recommended. Give them a shot! Check it out: gem88bet
Yo, BY88Club! Been hitting you guys up for a while now. Love the selection of games, and the payouts are pretty quick. Sometimes the site can be a bit laggy, but overall, it’s a solid place to try your luck. Definitely worth a shot! Check it out: by88club
Need a quick link to jljl1? jljl1link saved me a bunch of time. Very handy when you are eager to get playing. jljl1link
ok89bet is pretty okay. Not the best but it is not bad, especially for beginners I reckon! Give it a try. ok89bet
Alright guys, gotta say, ee881 is where it’s at lately! Been having some good luck over there. Give it a go! Check it out here: ee881