Stroke can change lives in an instant. It often leaves patients facing new challenges. Recovery is a journey that requires patience and support.
Occupational therapy plays a vital role in this journey. It helps stroke patients regain independence. The focus is on improving daily life skills.
Therapists work with patients to set achievable goals. These goals are tailored to individual needs. They aim to enhance mobility, self-care, and social participation.
Exercises and activities are key components of therapy. They help improve strength, coordination, and cognitive skills. Each session is a step toward recovery.
Hemiplegia, a common stroke outcome, affects one side of the body. Occupational therapy addresses this with targeted activities. These activities aim to restore function and confidence.
Family involvement is crucial in therapy. It provides motivation and support. Together, they create a nurturing environment for recovery.
Emerging technologies are enhancing therapy outcomes. Virtual reality and robotics offer new possibilities. They make therapy more engaging and effective.
Occupational therapy is more than physical recovery. It addresses emotional and social well-being. The goal is to improve quality of life for stroke patients.
Understanding Stroke and Its Impact on Daily Life
A stroke occurs when blood flow to the brain is interrupted. This can lead to serious physical and cognitive deficits. The effects can vary widely among patients.
Many stroke patients experience muscle weakness or paralysis. This often affects one side of the body, known as hemiplegia. Daily tasks become difficult and require adaptation.
Cognitive changes may also occur. These can include memory loss, difficulty concentrating, and impaired judgment. Such changes make everyday decisions more challenging.
Emotional well-being is another aspect impacted by stroke. Patients can experience mood swings, depression, and anxiety. These feelings can hinder recovery efforts.
Recovery is a personal journey. Challenges faced by stroke patients are diverse. They impact various aspects of life, as shown below:
- Physical challenges: Mobility, strength, and coordination.
- Cognitive challenges: Memory, concentration, and problem-solving.
- Emotional challenges: Anxiety, depression, and frustration.
- Social challenges: Interacting with others and participating in community activities.
Understanding these impacts is vital. It forms the foundation for effective therapy and recovery. Addressing each aspect helps patients regain control over their lives.
What Is Occupational Therapy for Stroke Patients?
Occupational therapy focuses on helping stroke patients regain independence. It addresses both physical and cognitive challenges that arise post-stroke. Therapists design personalized plans for each patient.
These plans aim to improve everyday functions. They include exercises that restore motor skills and coordination. Therapists also address cognitive functions like memory and concentration.
Occupational therapy involves a holistic approach. It considers emotional and social needs as well. This comprehensive focus aids in achieving better rehabilitation outcomes.
Therapy sessions are interactive and engaging. Patients may participate in activities like:
- Fine motor tasks: Buttoning shirts, writing, or picking up small objects.
- Gross motor tasks: Walking, balancing, and sitting down safely.
- Cognitive tasks: Problem-solving exercises and memory games.
The therapy also educates patients and families on adaptive strategies. This includes the use of assistive devices. The goal is to maximize independence and improve quality of life. These efforts ensure stroke patients can navigate daily life with greater ease and confidence.
The Role of Occupational Therapy in Stroke Rehabilitation
Occupational therapy plays a vital role in stroke rehabilitation. It bridges the gap between medical treatment and everyday life. The goal is to enable patients to perform daily activities more independently.
Therapists assess a patient’s abilities and design tailored interventions. These interventions focus on enhancing both physical and mental capabilities. The therapist works closely with the patient to set achievable goals.
A key component of therapy is adaptability. Therapists teach patients how to use various techniques and assistive devices. This guidance helps patients overcome challenges specific to their conditions.
To maximize effectiveness, therapists often involve families in the process. Supportive family members boost motivation and engagement. They learn how to assist patients safely at home.
Here’s a glimpse into activities that can be part of rehabilitation:
- Strengthening exercises: Target muscle groups to improve movement.
- Coordination activities: Tasks to enhance control and precision.
- ADL training: Focus on bathing, dressing, and cooking safely.
- Cognitive activities: Improve focus and memory.
Innovative approaches, such as virtual reality, are now emerging in therapy settings. These technologies offer interactive and motivating experiences. Combining traditional and modern methods accelerates recovery and leads to better outcomes.
Common Challenges After Stroke: Hemiplegia and Beyond
Stroke can lead to a variety of challenges for survivors. One of the most common is hemiplegia. This condition involves paralysis on one side of the body.
Other hurdles include communication difficulties and cognitive impairments. These can affect a patient’s ability to interact and solve problems. Emotional changes, like depression and anxiety, can also arise.
Balance issues and muscle weakness pose additional obstacles. They increase the risk of falls and limit mobility. Sensory deficits might alter how a patient perceives touch or temperature.
Therapists focus on addressing these diverse challenges:
- Motor skill retraining: Improve movement and coordination.
- Speech therapy: Help with communication barriers.
- Cognitive exercises: Enhance memory and problem-solving.
- Emotional support: Address mental health needs.
By tackling these concerns, occupational therapy aims to restore independence. Each patient receives individualized care designed to meet their unique needs. As they progress, therapy goals are adjusted to reflect new capabilities. This flexibility supports long-term recovery and quality of life.
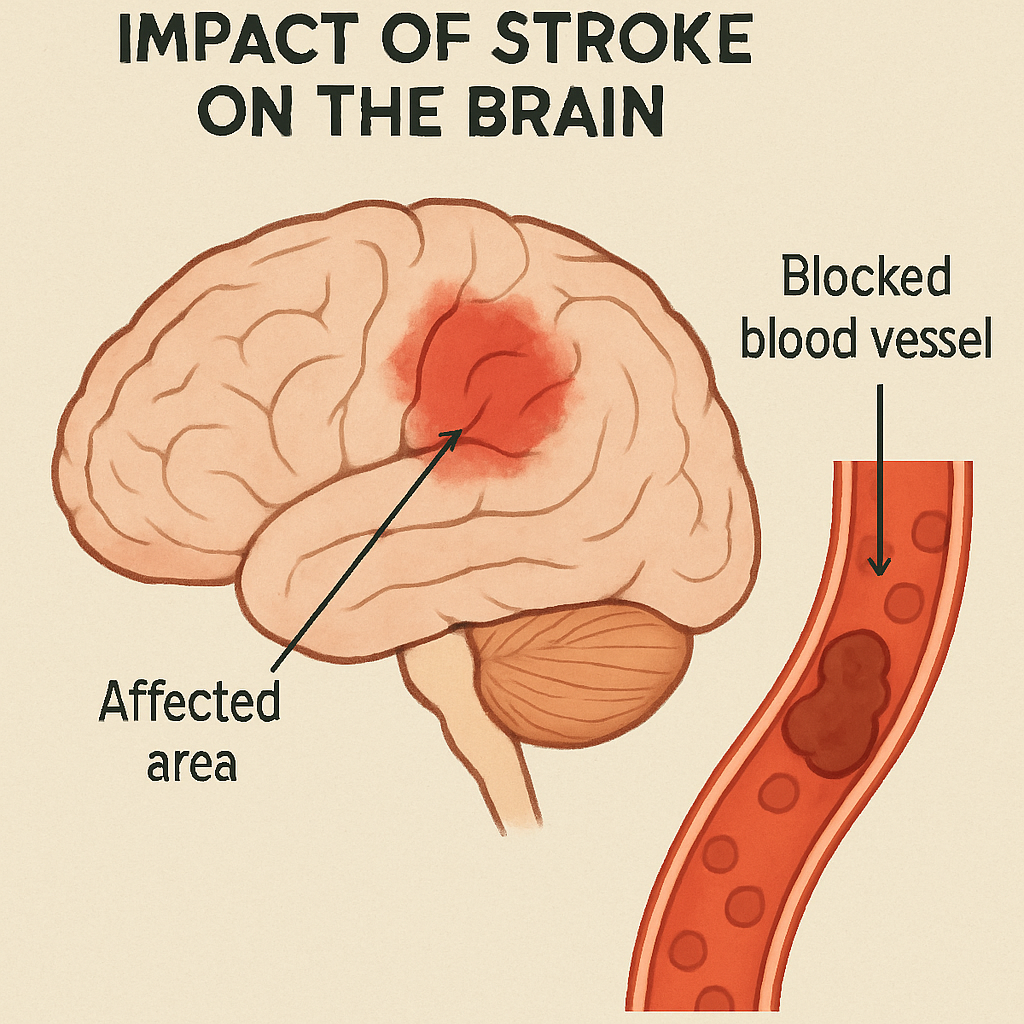
Setting Occupational Therapy Goals for Stroke Patients
Establishing goals in occupational therapy is crucial for stroke recovery. Goals guide the therapeutic process and measure progress. They should be clear, realistic, and personalized.
Therapists work closely with patients to identify their priorities. Patient involvement ensures the goals align with their daily life needs. It boosts motivation and engagement in therapy sessions.
Short-term Goals Focused On:
- Basic self-care tasks: Dressing, grooming, bathing
- Improving mobility: Walking short distances, navigating stairs
- Relearning motor skills: Grasping small objects, simple exercises
Long-term Goals May Include:
- Enhanced independence: Performing household chores, cooking meals
- Social participation: Attending family gatherings, community events
- Career reintegration: Returning to work or engaging in new job roles
Goals adapt as the patient progresses through different recovery stages. Flexibility allows for new challenges and accomplishments. Regular assessments ensure that therapy remains effective and relevant.
These tailored goals empower stroke patients. They encourage a sense of achievement and forward momentum. By structuring therapy around individualized objectives, therapists foster recovery, independence, and improved quality of life.
Examples of Occupational Therapy Goals for Stroke Patients
Occupational therapy goals for stroke patients are tailored to individual needs. They serve to enhance functionality in daily life. Here are examples across various domains.
Physical Goals:
- Enhance hand strength: Lifting weighted objects gradually
- Improve balance: Performing stand-alone exercises without support
- Increase range of motion: Completing full arm stretches
Physical goals help regain independence. They focus on rebuilding motor skills necessary for daily tasks. Achieving these goals can significantly impact a patient’s quality of life.
Cognitive Goals:
- Boost memory recall: Remembering daily schedules and names
- Enhance problem-solving skills: Completing puzzles or following multi-step instructions
- Strengthen attention span: Focusing on tasks for longer periods
Cognitive goals address changes due to stroke. They support mental agility and adaptation to lifestyle changes. Such improvements are vital for handling day-to-day activities.
Social and emotional goals can also be included. Therapists might target improving social interaction or managing emotions. These aspects contribute to a holistic recovery approach.
Effective goal setting in occupational therapy considers the whole person. It supports their physical, mental, and social wellbeing. By achieving goals, stroke patients can lead a more fulfilling life.
Occupational Therapy Activities for Hemiplegia Adults
Hemiplegia is a common challenge for stroke survivors. It often leaves one side of the body weakened or paralyzed. Occupational therapy addresses these issues through targeted activities.
Therapists use activities to improve motor functions. These activities are designed to stimulate the affected side. Repetition and consistency play a key role.
Core Activities Include:
- Arm lifts and rotations
- Hand and finger stretching exercises
- Supported leg lifts
These exercises aim to enhance flexibility. They also help restore strength. Over time, patients may notice improved coordination.
Beyond motor activities, therapy also focuses on daily living skills. This helps restore independence for adults with hemiplegia. Tasks often simulate real-life scenarios.
Daily Living Activities:
- Buttoning shirts and zipping jackets
- Practicing grasp and release with household items
- Using adaptive utensils for eating
Therapists tailor activities to each person’s capabilities. The goal is to foster autonomy despite physical limitations.
Therapists often integrate creative methods. Art or music can be therapeutic, providing joy and motivation. Such activities engage both the body and mind. Ultimately, occupational therapy supports recovery and self-sufficiency for adults facing hemiplegia.
Occupational Therapy Activities for Stroke Patients: Practical Approaches
Stroke can significantly impact daily life. Occupational therapy uses practical activities to help patients regain functionality. These activities are essential for rehabilitation and improving the quality of life.
Therapists focus on tasks that mimic daily routines. This approach helps patients relearn skills needed for independence. Each activity is designed to be engaging and purposeful.
Everyday Activities Include:
- Cooking simple meals
- Managing personal hygiene
- Organizing and sorting household items
These tasks help improve both physical and cognitive abilities. By simulating real-world scenarios, patients gain confidence. Each small victory contributes to larger recovery milestones.
In addition to daily activities, exercise is fundamental. Physical exercises are tailored to each patient’s needs. These routines are crucial for enhancing mobility and strength.
Exercise Examples:
- Walking exercises for balance
- Seated leg lifts to build muscle
- Arm exercises for range of motion
Therapists strive to keep these exercises enjoyable. Variety in activities fosters motivation and engagement. Engaging the senses can speed up healing.
Finally, therapy encourages creativity. Activities like drawing or crafting introduce fun while improving dexterity. These practices can also support emotional recovery. Occupational therapy provides a holistic approach to help stroke survivors regain control and autonomy in their lives.
Occupational Therapy Exercises for Stroke Patients: Step-by-Step Examples
Occupational therapy exercises are a cornerstone of stroke rehabilitation. These exercises are carefully selected based on individual needs. They aim to improve motor function, coordination, and daily living skills.
Strength and Mobility Exercises
- Arm Lifts: Start seated. Raise your affected arm using the other hand. Hold for five seconds.
- Leg Bends: Lie flat. Bend your knee slowly. Keep your foot flat on the floor.
Both exercises promote joint flexibility. Repetition enhances muscle memory and coordination. Gradual progress is vital for effective recovery.
Hand and Finger Coordination
- Finger Taps: Touch each finger to thumb in succession. Start slow, then speed up.
- Palm Opening: Gently spread fingers out and close back into a fist.
These exercises help with fine motor skills. They’re essential for tasks like writing or buttoning a shirt. Consistency is key to restoring dexterity.
Balance and Core Stability
- Seated Balance: Sit tall, feet flat. Shift weight side to side.
- Core Tightening: Contract abdominal muscles, hold, then release.
Activities like these strengthen the core and improve posture. They support functional movements, reducing fall risks. Balance exercises can be done multiple times daily.
Therapists provide continuous guidance. Techniques may adapt as patients improve. Motivation and encouragement are pivotal throughout recovery. These exercises help pave the path to independence, empowering stroke survivors to reclaim their lives.
Stroke Recovery Exercises: Building Strength and Coordination
Stroke recovery is a journey. It involves a variety of exercises designed to build strength and improve coordination. These are vital for regaining independence.
Lower Body Exercises
- Leg Raises: Sit on a chair. Slowly lift one leg at a time.
- Heel Lifts: Stand and rise onto your toes. Hold briefly, then lower.
These exercises bolster leg muscles. They support walking and balance. Regular practice is essential for progress.
Upper Body Workouts
- Shoulder Press: Use a lightweight object. Push upwards from shoulder height.
- Arm Circles: Extend arms to the sides and move in small circles.
These activities enhance upper body strength. They facilitate daily tasks like reaching and lifting. Consistent effort helps to rebuild muscle tone.
Coordination is crucial for fluid movements. Fine-tuning such movements can increase efficiency in daily life. Therapists may customize these exercises based on individual needs.
Improvements take time, but persistence pays off. Support from family and caregivers boosts motivation. Recovery is a team effort and requires patience and dedication. Regular assessment helps to track progress and adjust the therapeutic plan as needed, tailoring activities to maximize recovery and improve quality of life.
Cognitive and Sensory Occupational Therapy Activities
Cognitive and sensory activities are crucial in stroke rehabilitation. They address issues like memory loss and sensory deficits. These activities nurture mental and physical aspects.
Enhancing Cognitive Abilities
Activities often include puzzles and memory games. These tasks challenge the mind and boost recall.
- Memory Games: Use cards or apps to test and improve memory.
- Problem Solving: Engage in simple puzzles to enhance logic skills.
These exercises stimulate cognitive functions. They aid in building focus and patience.
Sensory Integration Techniques
These techniques help patients adapt to sensory changes. Therapists may use different textures and temperatures to improve sensory perception.
- Textures Exploration: Touch and feel objects of varying textures.
- Temperature Contrast: Alternate between warm and cool items.
Combining cognitive and sensory activities enhances a patient’s quality of life. It also prepares them for better reintegration into daily routines. Continuous practice under professional guidance can lead to gradual improvement. Family involvement can enrich these activities, making therapy a positive experience.
Adaptive Equipment and Home Modifications
Adaptive equipment can significantly aid stroke recovery. These tools promote independence in daily activities.
Importance of Adaptive Tools
Using the right equipment can facilitate movement and reduce the risk of injury. They enhance a person’s ability to perform everyday tasks efficiently.
- Grab Bars: Installed in bathrooms for stability.
- Reachers: Help in picking up objects without bending.
- Shower Chairs: Provide support while bathing.
- Non-slip Mats: Prevent falls, especially in wet areas.
- Built-up Utensils: Eased grip for those with weak grip strength.
Home Modifications for Safety
Simple home changes can foster a safer environment. Installing ramps or widening doorways aids mobility. Removing clutter ensures clear pathways, minimizing tripping hazards.
Both equipment and modifications tailor daily living to suit stroke survivors’ needs. These changes not only improve accessibility but also bolster confidence. Collaboration with occupational therapists can help in selecting appropriate modifications. These strategies collectively foster a supportive and safe living space.
The Importance of Family and Caregiver Involvement
Family and caregivers hold an essential role in stroke rehabilitation. Their support can dramatically influence recovery outcomes.
A collaborative approach benefits the patient and the caregivers. Informed caregivers provide better assistance. They can help reinforce therapy exercises. Active involvement fosters a supportive environment, contributing to emotional and social well-being.
- Encouragement: Boosts motivation and confidence.
- Consistency: Reinforces the therapy process at home.
- Observation: Identifies improvements and setbacks.
By engaging in therapy sessions, family members gain insights. They learn techniques to support recovery. This participation helps create a nurturing and encouraging atmosphere. Ultimately, a strong support network can significantly enhance a stroke patient’s path to recovery.
Emerging Technologies in Occupational Therapy for Stroke
Advancements in technology are transforming occupational therapy for stroke patients. These innovations offer new avenues for recovery. Therapists are embracing these tools to enhance patient outcomes.
Virtual reality (VR) provides an immersive environment for therapy. It allows patients to practice daily tasks in a controlled setting. VR can be tailored to individual needs, making therapy more engaging.
Robotics is another emerging field in stroke rehabilitation. Robotic-assisted devices aid in movement and strength training. These machines help improve motor function and coordination.
- VR and AR: Immersive and interactive experiences.
- Robotics: Precision movement and repetition.
- Telehealth: Remote therapy sessions increase accessibility.
These technologies promise a bright future for stroke rehabilitation. They offer innovative solutions to traditional challenges. Adopting such tools can significantly boost recovery potential.
Emotional and Social Well-Being in Stroke Rehabilitation
Stroke impacts emotional health and social interaction. Rehabilitation should address these vital components. Patients benefit from a holistic approach focusing on overall well-being.
Emotional support is crucial during recovery. Depression and anxiety are common challenges. Therapy can include counseling and stress-reduction techniques. These aid in managing emotions effectively.
Social connections significantly impact recovery. Encouraging social participation can improve mood and motivation. Therapists often incorporate group activities to foster interaction.
- Counseling: Provides emotional coping strategies.
- Group therapy: Builds social networks and support.
- Stress reduction: Techniques like mindfulness and relaxation exercises.
Focusing on emotional and social health enhances rehabilitation. Patients gain confidence and a sense of belonging. This holistic care fosters resilience and independence.
Tips for Maximizing Progress in Occupational Therapy
Making the most out of occupational therapy requires dedication and strategy. Here are some tips to help you optimize your rehabilitation journey.
Being consistent with therapy sessions is key. Regular attendance ensures steady progress and adaptation to your evolving needs. Set realistic goals to maintain motivation. Achieving small milestones can boost confidence and encourage continued effort.
Engaging family members can provide crucial support. Their involvement often enhances motivation and accountability. Creating a supportive home environment also aids recovery.
- Consistency: Attend sessions regularly.
- Goal setting: Focus on achievable milestones.
- Family support: Involve loved ones for encouragement.
Communicate openly with your therapist. Discuss any concerns or changes in your condition. This collaboration helps tailor the therapy to best suit your needs, enhancing overall progress.
Frequently Asked Questions About Occupational Therapy for Stroke Patients
Stroke patients and their families often have numerous questions. Here are answers to some of the most common inquiries.
How soon after a stroke should occupational therapy start?
Therapy usually begins as early as possible. Early intervention often leads to better outcomes.
What is the duration of occupational therapy for stroke patients?
The length depends on individual needs and progress. It can range from weeks to several months.
Can occupational therapy be done at home?
Yes, many exercises can be adapted for home use. This encourages daily practice and consistency.
Is occupational therapy painful?
While therapy can be challenging, it shouldn’t be painful. Always communicate discomfort to your therapist.
- Early Start: Begin therapy soon after a stroke.
- Duration: Varies based on progress.
- Home Therapy: Many activities are adaptable.
- Pain: Shouldn’t be part of therapy.
What support is available for caregivers?
Support groups and resources are accessible for those supporting stroke patients. They provide valuable guidance.
Conclusion: The Path to Independence and Quality of Life
Occupational therapy plays a crucial role in stroke recovery. It empowers patients to regain independence and enhance their quality of life.
Through personalized exercises and goals, patients steadily improve daily function. This progress fosters both physical and emotional resilience.
The journey of stroke rehabilitation requires persistence, but the rewards are significant. As patients progress, they gain not only mobility but also confidence in their capabilities.




https://shorturl.fm/nSNzg
https://shorturl.fm/YJgyO
https://shorturl.fm/5iZW6
https://shorturl.fm/nrRyu
https://shorturl.fm/tiTDM
https://shorturl.fm/2AmLK
https://shorturl.fm/s8m8E
https://shorturl.fm/HjWev
https://shorturl.fm/3IhxW
https://shorturl.fm/eJR5c
Confesso que me viciei no phbest! A navegabilidade do site e otima e a variedade de jogos disponiveis e enorme. Sempre encontro algo novo pra jogar. E os bonus, nem se fala! So alegria! phbest
Phdream6 e onde a diversao nao tem fim! Os graficos sao incriveis e a atmosfera dos jogos e envolvente. Se voce procura uma experiencia imersiva, essa e a plataforma certa! Experimente! phdream6
Phjoylogin e a plataforma que me da mais alegria! Os jogos sao super divertidos e desafiadores. Sempre me sinto recompensado ao jogar por la. Nao perca tempo e venha se divertir tambem! phjoylogin
Decided to try 639club today. Had a good run on the slots. Nice and easy to use. Worth having a gander, innit? Go give it a go: 639club
Yo, checking out jljl999! It’s got that classic vibe, you know? Could be a good spot to unwind after a long day. Have a look-see: jljl999
Got my eye on these Playtime Apps. Seems like an easy way to kill some time and maybe win a little something. Check out their app selection here: playtime apps
Yo, check out 74betcom! They’ve got a decent selection of games, and I’ve seen some of my buddies actually cash out real money. Don’t go betting the house, but it’s fun for a casual gamble. Give it a looksee 74betcom
Alright, lemme tell ya about dlrbet. Nothing super special, but it’s got a decent selection of your usual slots and table games. If you’re passing through, give it a spin. You might get lucky. Time to get betting, give dlrbet a try.
Okay y’all, bcasino has a alright selection. Nothing really crazy. Just be responsible and you should have fun. Try it! bcasino.